2025-04-09
Spring Entity Mapping
Spring Framework (6)

Spring Entity Mapping

Spring Framework

데이터베이스에는 많은 테이블, 테이블간 여러 관계를 가짐
이것을 JPA/Hibernate로 설계 해야함
관계의 다중성에는 네 가지 유형이 있음
@OneToOne@OneToMany, @ManyToOne@ManyToMany관계의 방향은 다음과 같을 수 있음
주인 쪽(owning side)은 참조를 테이블에 실제로 저장하는 엔터티 즉 외래 키(foreign key)를 가진 테이블
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY)Cascading 업데이트/삭제
ALL, PERSIST, , , MERGEREMOVEREFRESH| Cascade Type | 설명 | 적용되는 작업 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 모든 작업(저장, 업데이트, 삭제 등)이 자식 엔티티에 전파됨. | 부모의 persist, merge, remove, refresh, detach 작업 모두 자식 엔티티에 전파 (영속성 컨텍스트에서만 적용) |
| PERSIST | 부모 엔티티가 영속화(persist)될 때 자식 엔티티도 영속화됨. | 부모의 persist 작업이 자식 엔티티에 전파됨 (영속성 컨텍스트에서만 적용) |
| MERGE | 부모 엔티티가 병합(merge)될 때 자식 엔티티도 병합됨. | 부모의 merge 작업이 자식 엔티티에 전파됨 (영속성 컨텍스트에서만 적용) |
| REMOVE | 부모 엔티티가 삭제(remove)될 때 자식 엔티티도 삭제됨. | 부모의 remove 작업이 자식 엔티티에 전파됨 (영속성 컨텍스트에서만 적용) |
| REFRESH | 부모 엔티티가 새로 고침(refresh)될 때 자식 엔티티도 새로 고침됨. | 부모의 refresh 작업이 자식 엔티티에 전파됨 (영속성 컨텍스트에서만 적용) |
| DETACH | 부모 엔티티가 분리(detach)될 때 자식 엔티티도 분리됨. | 부모의 detach 작업이 자식 엔티티에 전파됨 (영속성 컨텍스트에서만 적용) |
※ 기본적으로는 어떠한 작업도 연쇄되지 않음
연관된 엔터티를 가져오는 전략(Fetching strategy)
LAZY, EAGER※ 즉, 프로퍼티에 접근할 때까지 해당 행(row)을 로드하지 않음
| Mapping | Default Fetch Type |
|---|---|
@OneToOne | FetchType.EAGER |
@OneToMany | FetchType.LAZY |
@ManyToOne | FetchType.EAGER |
@ManyToMany | FetchType.LAZY |
Many가 포함되면 FetchType.LAZY가 Default
한 강사는 여러 강의를 가질 수 있다.
+----------+
* --- | Course |
| +----------+
|
+-------------+ | +----------+
| Instructor | <-- + --- | Course |
+-------------+ | +----------+
|
| +----------+
* --- | Course |
+----------+@Entity
@Table(name="instructor")
public class Instructor {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name="id")
private Long id;
@Column(name="full_name")
private String fullName;
@Column(name="email")
private String email;
}@Entity
@Table(name="course")
public class Course {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name="id")
private Long id;
@Column(name="title")
private String title;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="instructor_id")
private Instructor instructor;
}@ManyToOne 애너테이션을 사용하여 JPA/Hibernate에게 어떤 객체가 자식 객체인지 알려줄 수 있습니다.@OneToMany 애너테이션을 사용하여 JPA/Hibernate에게 어떤 객체가 부모 객체인지 알려줄 수 있습니다.@JoinColumn 애너테이션을 사용하면, 어떤 컬럼을 조인에 사용할지 명시할 수 있으며, 해당 컬럼의 이름도 지정할 수 있습니다.※ 즉, 부모 테이블(instructor), 자식 테이블(course) 중에서, 자식 테이블이 외래 키를 가짐
@Repository
@Transactional
public class CourseDao {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void save(Course course) {
entityManager.persist(course);
}
public Course findById(Long id) {
return entityManager.find(Course.class, id);
}
public List<Course> findAll() {
return entityManager.createQuery("SELECT c FROM Course c", Course.class).getResultList();
}
}@Repository
@Transactional
public class InstructorDao {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void save(Instructor instructor) {
entityManager.persist(instructor);
}
public Instructor findById(Long id) {
return entityManager.find(Instructor.class, id);
}
public List<Instructor> findAll() {
return entityManager.createQuery("SELECT i FROM Instructor i", Instructor.class).getResultList();
}
}// [1] Instructor 객체 생성
Instructor instructor1 = new Instructor("Namyun Kim", "nykim@hansung.ac.kr");
Instructor instructor2 = new Instructor("Jaemon Lee", "jmlee@hansung.ac.kr");
// [2] Instructor 먼저 저장 (DB에 insert + id 생성)
instructorDao.save(instructor1);
instructorDao.save(instructor2);
// [3] Course 객체 생성
Course course1 = new Course("웹프레임워크");
Course course2 = new Course("오픈소스소프트웨어");
Course course3 = new Course("iOS 프로그래밍");
Course course4 = new Course("안드로이드 프로그래밍");
// [4] 각 Course에 Instructor 설정 (연관관계 주입)
course1.setInstructor(instructor1);
course2.setInstructor(instructor1);
course3.setInstructor(instructor2);
course4.setInstructor(instructor2);
// [5] Course 저장 (instructor_id 포함된 상태로 INSERT)
courseDao.save(course1);
courseDao.save(course2);
courseDao.save(course3);
courseDao.save(course4);※ 데이터베이스 변경 X, 단지 Java 코드만 업데이트
@Entity
@Table(name="instructor")
public class Instructor {
…
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "instructor",fetch = FetchType.LAZY, cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
private List<Course> courses = new ArrayList<>();
// 연관 관계 편의 메소드
public void addCourse(Course course) {
courses.add(course);
course.setInstructor(this);
}
}instructor 속성을 참고하라 알림public class Instructor {
...
@OneToMany(mappedBy="Instructor")
private List<Course> courses;
}public class Course{
...
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="instructor_Id")
private Instructor instructor
}이 연관관계의 주인은 Course 쪽의 instructor 필드
Instructor instructor1 = new Instructor("Namyun Kim", "nykim@hansung.ac.kr");
Course course1 = new Course("웹프레임워크");
Course course2 = new Course("오픈소스소프트웨어");
instructor1.addCourse(course1);
instructor1.addCourse(course2);
// cascade=CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY
instructorDao.save(instructor1);
// 저장된 Instructor 조회 및 결과 확인
Instructor retrievedInstructor = instructorDao.findById(instructor1.getId());
System.out.println("Instructor: " + retrievedInstructor.getFullName());
for (Course Course : retrievedInstructor.getCourses()) {
System.out.println("Course: " + Course.getTitle());
}@Transactional이 끝나면 EntityManager(DB 연결)가 닫히기에 지연로딩(LAZY)된 연관 객체는 더 이상 불러올 수 없음@Transactional
public Instructor findByIdWithCourses(Long id) {
Instructor instructor = entityManager.find(Instructor.class, id);
if (instructor != null) {
instructor.getCourses().size(); // 컬렉션 로드
}
return instructor;
}+-------------+ +--------------------+
| Instructor | --------> | InstructorDetail |
+-------------+ +--------------------+@Entity
@Table(name="instructor_detail")
public class InstructorDetail {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "youtube_channel")
private String youtubeChannel;
@Column(name = "hobby")
private String hobby;
}@Entity
@Table(name="instructor")
public class Instructor {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
private Long id;
…
@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "instructor_detail_id")
private InstructorDetail instructorDetail;
}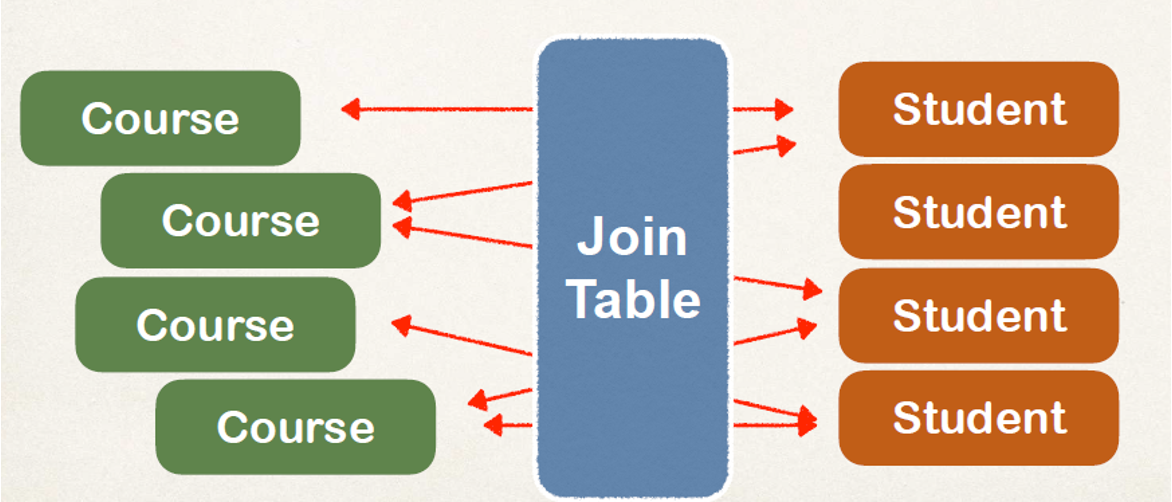 Many To Many
Many To Many
Join Table을 두고 관계를 유지하는 것이 효율적
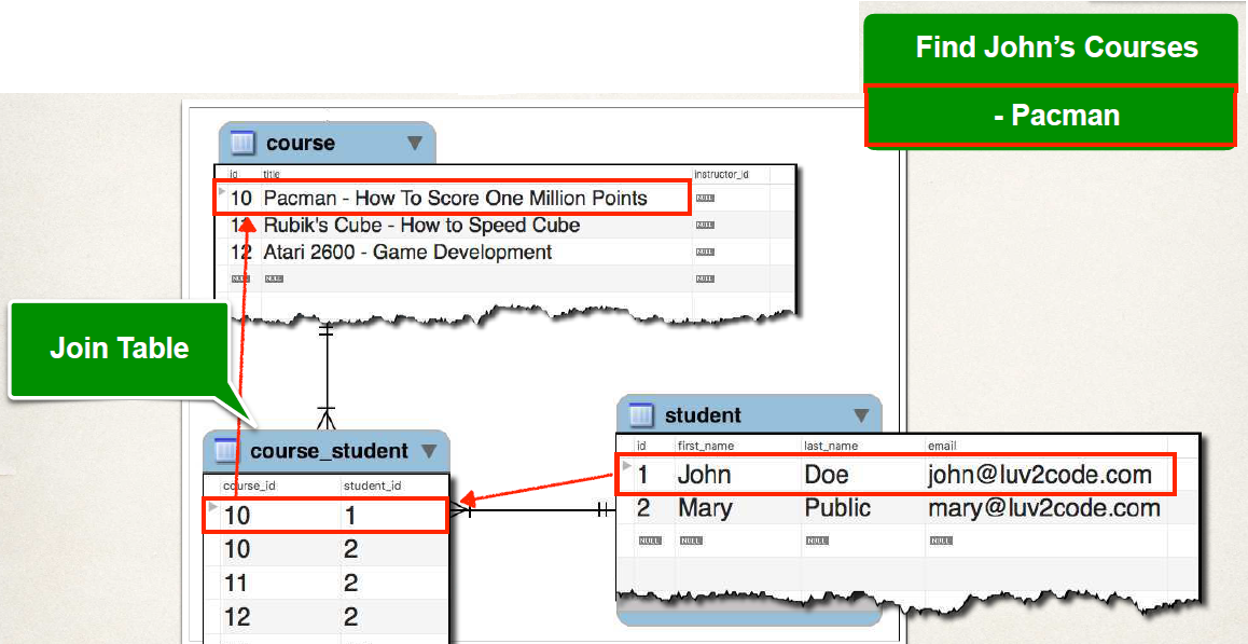 Many To Many
Many To Many
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
...
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(
name = "student_course",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "student_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "course_id")
)
private List<Course> courses;
}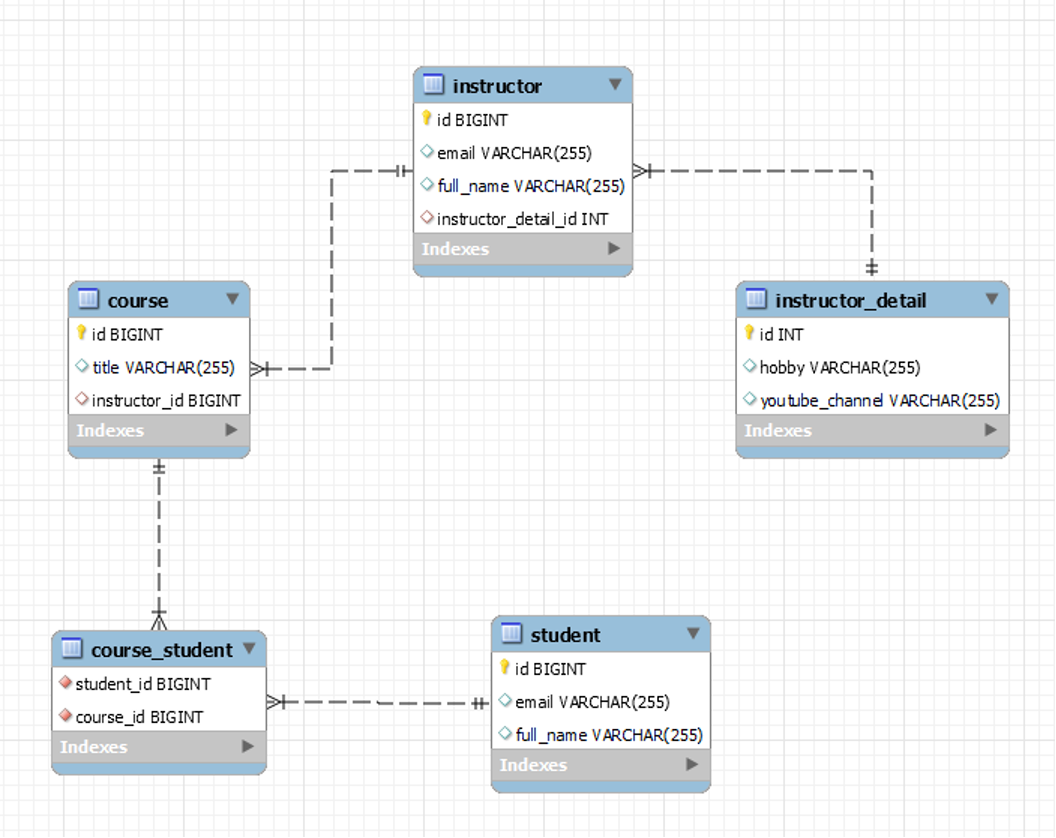 Architecture
Architecture